As the world is becoming increasingly digital and financially complex, it is imperative to teach children good financial habits early in life. Opening and managing a savings account is an effective way to introduce kids to the intriguing world of finance. We will analyse the importance of teaching children financial responsibility and offer practical tips on how to save and manage a savings account, setting them on the path to a secure financial future.
Financial responsibility is one of the most important skills to bequeath your child, if taught early in life, the kids go on to become financially responsible adults who are well-grounded in money management and other aspects of financial management, such as, saving, budgeting, delayed gratification, prudent spending, and investing for the future.
Benefits of Early Financial Education
Setting the foundation for financial literacy
Financial literacy is a skill that can benefit people throughout their lives. Teaching children about money from a young age sets the groundwork for a solid financial future. Exposing children to fundamental financial concepts like earning from honest work, saving, and spending teaches children the value of money and the importance of making sound financial decisions
Promoting financial responsibility and independence
Exposing kids to the complex world of finance by opening a savings account for them, promotes responsibility and independence. Creating a budget, setting goals and practicing delayed gratification are all essential life skills that children develop as they learn to manage their finances. These skills are not only useful for their current situation but also helps them succeed in the future.
Making informed decisions
Kids who are taught financial literacy early grow up to become better decision-makers, they know how to use the data available to them to make informed decisions about financial planning and money management
Better understanding of the digital landscape
In this digital age, most financial transactions are done online. Teaching children about savings by exposing them to digital banking platforms such as Mintyn. Making them more comfortable navigating the digital landscape. This early exposure equips them with the tools they will need as adults, ensuring that they manage their finances effectively.
What is a Savings Account

A savings account is a type of deposit account operated by banks and other financial institutions that yields interest. The interest paid on them is usually little but they are safe, reliable and easy to manage making them an excellent choice for storing cash for short-term use.
Some banks put restrictions on the savings account in order to limit the amount and frequency with which you can withdraw money. However, its flexibility makes it an ideal source of emergency funds, it is also a way to store money to meet short and medium-term goals like school fees, healthcare, and so on.
Understanding the Various Types of Savings Account
Before we delve into savings account tips, it is important to understand that there are several kinds of savings accounts obtainable for children. Normal/traditional savings accounts, custodial accounts, high-yield savings accounts, and educational savings accounts all have their own features and restrictions. Having a proper understanding allows parents to select the account that is most suitable and that aligns with the financial goals they have for their child.
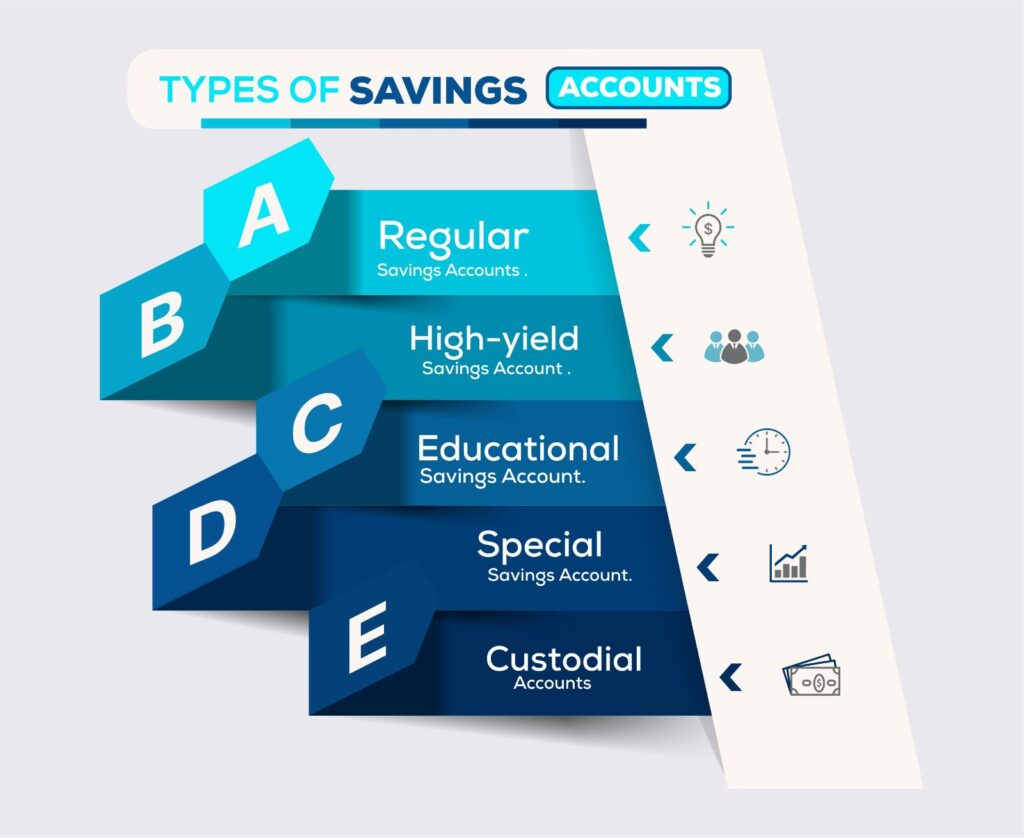
Regular Savings Account
When you think of opening a savings account, the regular savings account readily comes to mind, it is obtainable at most commercial banks and financial institutions. Banks pay interest on your money when you operate this account. Although the interest rates are slightly lower than what is obtainable for other savings products offered by banks,. Most banks offer incentives for customers willing to open a regular savings account, such as free debit /ATM cards.
High-Yield Savings Account
This type of savings account allows you to earn a higher interest rate on your money than you would with a regular savings account. This account is preferred by those who want to maximise the interest payable. Alongside providing better interest rates, they also offer fewer fees for account maintenance and have a larger withdrawal limit.
Special Savings Account
This is actually where our focus is. This type of savings account is ideal for individuals who have a particular savings objective. There are different types of special savings accounts, such as:
- Children’s Savings Account
- Educational Savings Account
- Medical Emergency Savings account
- Custodial accounts
- Retirement Savings Account
Children’s savings accounts are typically opened by parents on behalf of their children. It encourages them to save and promotes better money management. Parents can show the kids their bank statements periodically so that they can see how their money is growing. Many banks offer this type of savings account and regularly organise fun fares for children to sensitise them about saving and to market the account type to their parents.
Educational savings accounts: are special accounts that parents can operate to help offset the tuition and school fees of their children. Some parents open these accounts when their children are born and continue to save money in it towards their university education. One of the incentives for opening an educational account is the ability to access emergency loans.
Custodial accounts: as the name implies, this type of account is set up on behalf of a child and managed by their parents or a legally appointed guardian. The child will have access to the account when he/she turns 18, depending on the laws of the state.
Factors to Consider When Opening a Savings Account
Interest rates and fees
In order to choose the right savings account for your child, it is critical to consider the interest rates and fees on the account. Parents should research, compare, and analyse these factors across different banks to ensure that they get the best out of the savings account and that the money can grow at an optimal rate. Many banks offer savings accounts specifically designed for kids with beneficial conditions that encourage children to enjoy the advantages of saving.
Unveiling the principle of compound interest
Most kids, by the time they are done with elementary school, have heard about simple interests. Now imagine putting this into practice by teaching them about compound interest and showing them how money can be multiplied and made to grow over time, especially if they are consistent with saving.
Tips for Teaching Financial Responsibility to Kids

Goals! Goals!! Goals!!!
Establish clear goals for saving; having a specific target gives the kids a sense of purpose and motivation. It will encourage them to remain consistent in saving, and they can plan for the things they love, like toys and gadgets, while their parents can rely on it for future educational expenditures. Periodically reviewing and modifying these goals teaches children the importance of revising their plans to match their current financial status.
Create a Savings Routine
The watchword is consistency; it is an essential financial habit. Encourage children to develop a saving routine, such as keeping part of their allowance or other monetary gifts from their parents. This will instil discipline and help them stay on track to achieve their financial goals.
Be the example
One of the greatest ways in which children learn is through observation. Research by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) found that financial habits are formed in children between the ages of 3-12. Children observe their parents to see how they handle money, how they spend money, and how they make financial plans. It is important to set a good example for your kids to follow. If they observe that you have good money management, they are likely to follow in your footsteps as they grow older.
Explain the concept of opportunity cost
Opportunity cost simply means forgoing one thing for another. Take time to explain this concept to your kids. Let them understand that, for example, if you get the Lego toy, you will not get the video game. This will teach them to weigh their decisions and to choose wisely what is necessary at a particular time.
Teach the Value of contentment
Contentment is the state of being satisfied and happy. Teach your kids the value of being content and grateful for what they have so that they do not fall into the trap of comparing themselves with other kids and putting their parents under unnecessary pressure.
Help them create a budget
Budgeting helps control spending and assign limited funds to where they are most needed. Learning this skill early in life cannot be over-emphasized. Children must be taught how to plan for the funds they have, no matter how little they have.
Monitor and review progress
Regularly reviewing the progress made, helps keep kids on track and gives them a sense of accomplishment. Reviewing their progress helps identify areas for growth and if the saving strategy needs to be modified. Regular scrutiny encourages accountability and self-reflection. Parents can take advantage of these sessions to discuss milestones, address challenges, and celebrate successes, ultimately promoting good financial responsibility.
Spend wisely
Financial responsibility does not only entail saving, it is also about making wise decisions about spending. Teach kids to find the right balance between spending and saving; they should weigh different options before making a purchase. This will enable them to make informed spending decisions.
Discussing needs vs wants

Comprehending the distinction between needs and wants is a crucial aspect of financial literacy. Communicate with children about essential needs and unnecessary wants, this will help them prioritise their spending and allocate funds to things that are really important, thus promoting financial responsibility.
Furthermore, utilise every opportunity to teach financial responsibility, including when you have made mistakes. Sometimes mistakes are inevitable; it can be a wrong investment, inaccurate projections, or just financial decisions that become unfavourable. These experiences can become wonderful opportunities to learn and, invariably, teach. Instead of shying away from them, discuss mistakes openly with children, this will help them build resilience and better manage financial upheavals that may occur later in life.
As children grow older, it becomes imperative to introduce them to the value of making investments and teach them about stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Although a savings account is a stable and safe option for money management, taking calculated risks in the form of investments is also an aspect of financial responsibility. Teaching them early about investments broadens their understanding of the financial world and helps them make informed decisions in the future. However, keep it simple and relevant to their age.
As children mature, parents can gradually increase their financial responsibility, entrust them with dealing with a larger part of their expenditures, involve them in the decision-making process of how much to save, and introduce incentives like allowing them to earn money for doing some common household chores like mowing the lawn. They can get a part-time job or work during school holidays. They will gradually learn to become independent, thus paving the way for becoming adults who are financially literate and practice better money management
Teaching children the important skill of financial responsibility through opening a savings account for them is a rewarding investment in their future. By fostering good financial habits in their children early in life, parents can help them make smart choices, explore the digital financial environment, and ensure a secure financial future. These practical strategies will help parents guide their children towards financial literacy and responsibility. Parents have to provide the next generation with the necessary financial skills, which will ultimately help build a society that is stable and financially secure.








