“Interest grows the money while you set it aside in your savings account. How fast your money grows depends on the interest rates”
Cultivating a habit of saving is not just a prudent choice but a crucial aspect of personal financial management.
Savings serve as a financial cushion, providing you with the means to tackle unforeseen expenses, achieve long-term goals, and manage life’s uncertainties with greater confidence.
A savings account is ideal for many things: building an emergency fund, saving for a home, planning for retirement, etc.
At the heart of every savings strategy lies the concept of interest rates. Interest rates are the engines that drive the growth of savings accounts.
They determine the additional earnings your savings generate over time. Interest rates transform a stagnant sum into a flourishing asset.
Understanding how interest rates work is the key to realising the full potential of your savings.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the concept of interest rates and how it affects your savings.
The Basics of Interest Rates
Interest rates serve as the cost of borrowing or the return on investment for lenders.
In the context of savings accounts, they determine how much your money grows over time.
Simply put, when you deposit money into a savings account, the bank pays you interest as a reward for keeping your funds with them.
Types of Interest Rates
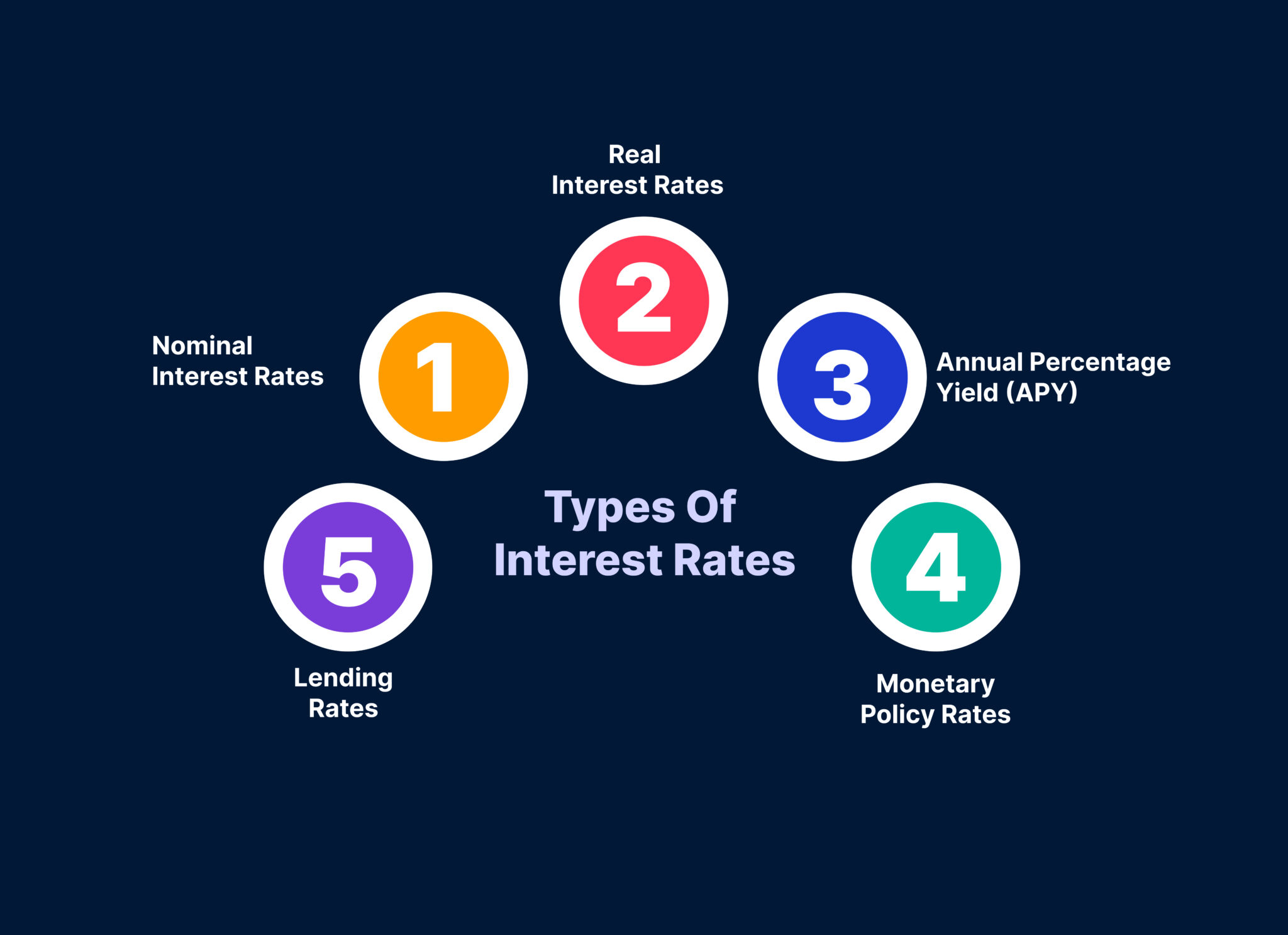
In Nigeria, the dynamics of interest rates play a crucial role in influencing savings growth in various accounts. Let’s now explore different types of interest rates:
1. Nominal Interest Rates
Nigerian banks offer nominal interest rates on savings accounts. This represents the baseline return on deposits. As a saver, you should look at these rates as a starting point for evaluating the potential growth of your savings.
The nominal interest rate is the “number” value and not necessarily the real or actual value when the inflation rate is considered.
Given Nigeria’s historical challenges with inflation, you must consider the real interest rate to assess the true purchasing power gained from your savings.
2. Real Interest Rates
Nigeria has experienced periods of high inflation. Therefore, you need to be mindful of the real interest rate to ensure that your savings outpace the inflation rate, preserving their purchasing power over time.
3. Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
Nigerian financial institutions often advertise savings products with an Annual Percentage Yield (APY). This reflects the total return on investment, including compound interest. This metric helps compare different accounts and make informed choices.
Understanding the compounding effect will benefit you, especially when considering long-term savings goals. The APY provides a holistic view of how savings can grow over time.
4. Monetary Policy Rates
The Central Bank of Nigeria sets the monetary policy rates, including the Monetary Policy Rate (MPR), which influences the overall interest rate environment. Changes in these rates can have cascading effects on interest rates across the financial sector.
The Central Bank’s decisions on interest rates aim to manage inflation, stimulate economic growth, and ensure financial stability. These decisions, in turn, affect the interest rates on savings accounts and other financial products.
5. Lending Rates
Prime Lending Rate: The Prime Lending Rate in Nigeria is a reference for commercial banks when determining loan interest rates. It indirectly influences the cost of borrowing and impacts the overall interest rate climate in the country.
Changes in lending rates can affect consumers, influencing the affordability of loans and, subsequently, impacting their financial decisions and savings strategies.
Understanding these different types of interest rates will help you to make informed decisions about your savings and investments.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates in Nigeria
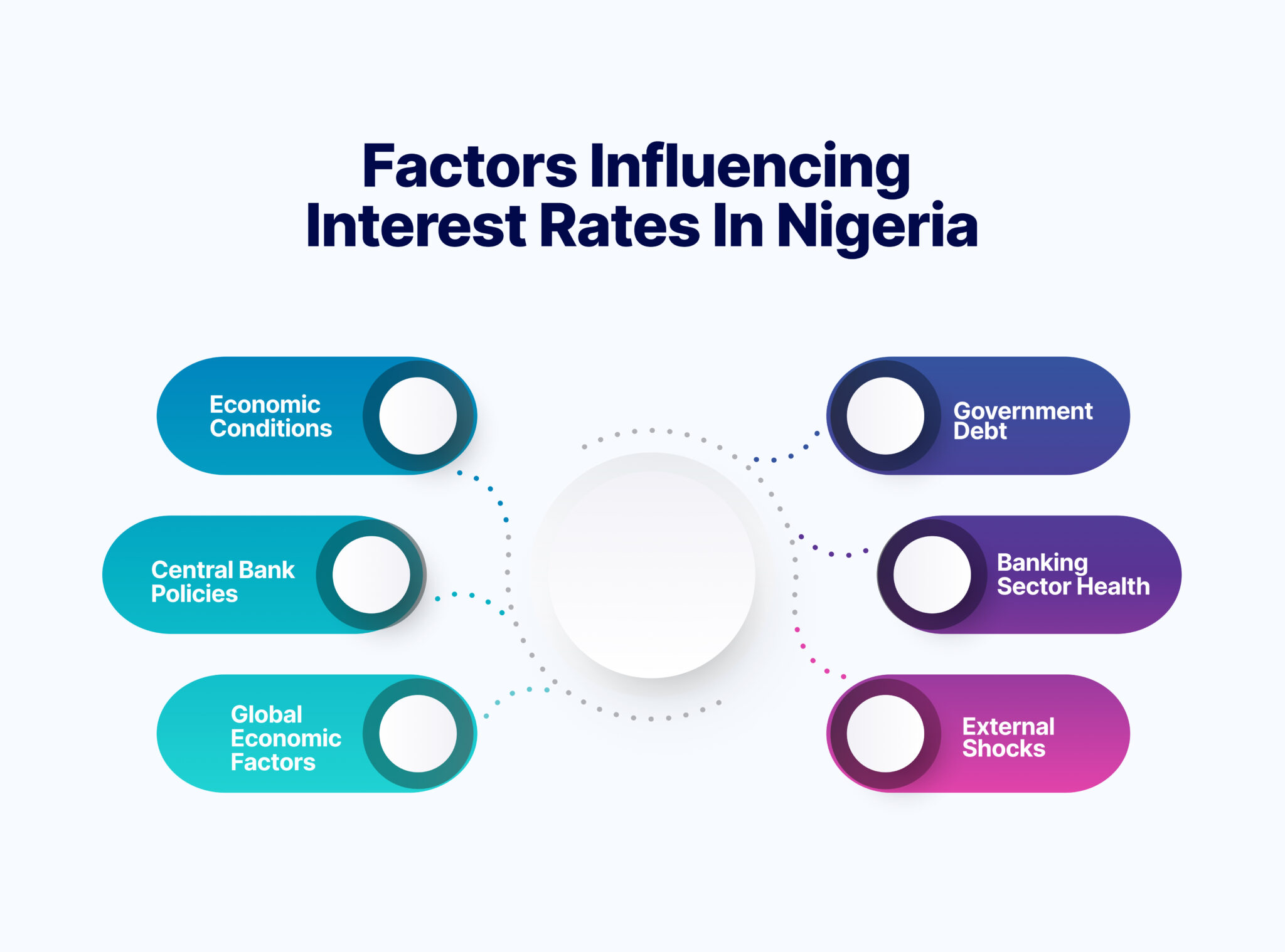
Understanding the factors that influence interest rates is important. Various economic conditions and policy decisions contribute to determining interest rates on savings accounts and other financial products.
Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Economic Conditions
Inflation Rates: Inflation rates play a significant role in determining nominal interest rates. The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) considers inflation targets when setting monetary policy rates.
Real Interest Rates: You must assess real interest rates by subtracting the inflation rate from nominal interest rates to ensure that your savings maintain or increase in purchasing power.
Expansionary Policies: During periods of economic growth, the central bank may implement expansionary monetary policies that influence interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending.
Lowering interest rates encourages borrowing and increases spending; increasing interest rates causes the opposite.
Demand for Credit: Increased demand for credit during economic expansions may lead to higher interest rates on loans and, subsequently, on savings accounts.
2. Central Bank Policies
Benchmark Rate: The Monetary Policy Rate (MPR), set by the CBN, serves as the benchmark interest rate in Nigeria. Changes in the MPR influence the overall interest rate environment.
Influence on Lending Rates: Commercial banks adjust their lending rates based on changes in the MPR. This impacts the rates offered on savings accounts.
Liquidity Management: The CBN may adjust reserve requirements for banks to manage liquidity in the financial system. Changes in reserve requirements can affect the availability of funds for lending, thereby influencing interest rates.
3. Global Economic Factors
Foreign Exchange Rates: Nigeria’s import-dependent economy makes it susceptible to changes in global commodity prices and exchange rates. Fluctuations can impact inflation rates. This, in turn, influences domestic interest rates.
Foreign Investment Impact: Changes in global economic conditions can affect foreign investment flows, influencing interest rates in Nigeria.
Global Interest Rate Trend: Global rate trends can influence capital flows into or out of Nigeria. Investors may seek higher returns in response to changes in interest rates globally, thus affecting domestic rates.
4. Government Debt
Issuance of Government Securities: When the government issues a significant amount of debt securities, it can lead to a “crowding out” effect, where the demand for funds increases, potentially raising interest rates.
Investor Attraction: The rates offered on government securities can attract investors, impacting overall interest rate levels in the financial market.
5. Banking Sector Health:
Liquidity Level: Banks’ liquidity positions influence their ability to lend. If liquidity is tight, banks may raise lending rates. This will affect interest rates across the financial sector.
Competitive Savings Rates: Banks’ competition for deposits can lead to attractive customer savings rates.
6. External Shocks:
Oil Price Volatility: As a major oil exporter, Nigeria is vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices. Oil price volatility can affect government revenue, trade balances, and inflation. All these influence rates.
Global Economic Crises: During global economic crises, investors may seek safer assets, impacting rates. Central banks may respond with policy measures that influence domestic rates.
Understanding these factors helps individuals anticipate changes in rates, enabling them to make informed decisions about savings and investments.
Monitoring economic indicators and staying informed about central bank policies are crucial for financial planning.
Risks and Considerations Associated With Savings Accounts
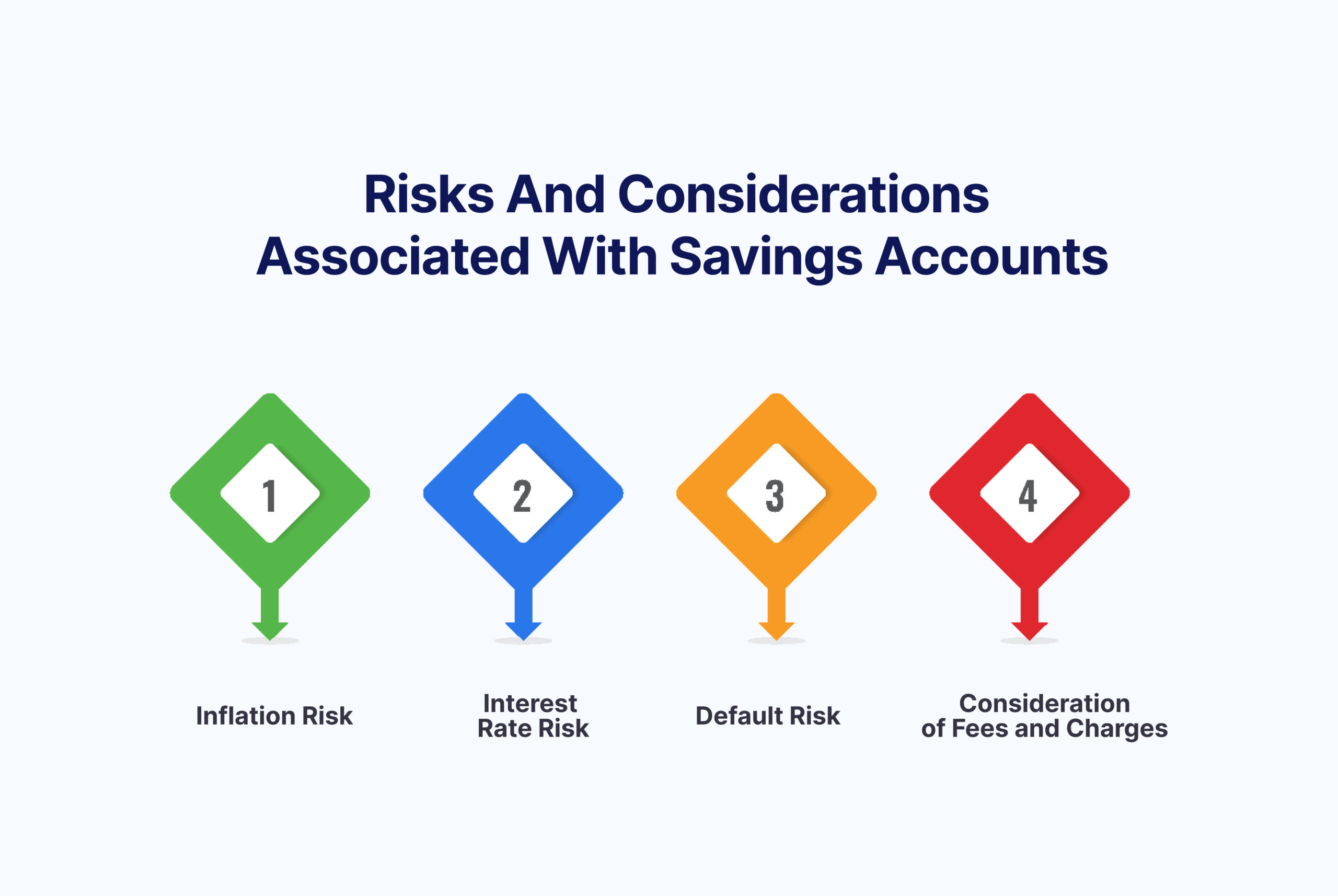
While savings accounts are generally considered low-risk financial instruments, you must be aware of potential risks and carefully consider certain factors.
This section outlines key risks associated with rates and offers considerations to help you make informed decisions about your savings account:
1. Inflation Risk
Impact on Purchasing Power: Inflation risk refers to the potential for the purchasing power of money to decline over time. If the nominal interest rate on your savings account does not outpace inflation, you may experience a decrease in real purchasing power.
Consider Real Interest Rates: You should assess real rates (nominal interest rate minus inflation) to ensure that your savings grow in real terms and maintain their value against the rising cost of living.
2. Interest Rate Risk
Fluctuations in Rates: Interest rate risk arises when there is uncertainty about future changes in rates. Fluctuations can impact the returns on savings accounts, especially in an environment where interest rates are subject to adjustments.
Fixed vs. Variable Rates: You should know whether your savings account has a fixed or variable rate. Fixed rates offer stability but may not adjust to favourable market conditions, while variable rates may change with economic factors.
3. Default Risk
Bank Stability: While savings accounts are generally considered safe, it’s essential to assess the stability and reputation of the bank. You should choose reputable institutions with a track record of financial strength.
Deposit Insurance: The Nigerian Deposit Insurance Corporation (NDIC) provides deposit insurance for savings accounts. You should confirm that their bank is covered by NDIC, which protects deposits up to a certain limit.
4. Fees and Charges
Account Maintenance Fees: Some savings accounts may have maintenance fees or charges for specific services. You should review the fee structure to understand the impact on overall returns.
Hidden Costs: Be vigilant about hidden costs that may affect the effective rate earned on savings. Reading the terms and conditions carefully helps in uncovering any potential surprises.
Tips for Maximising Your Savings Account
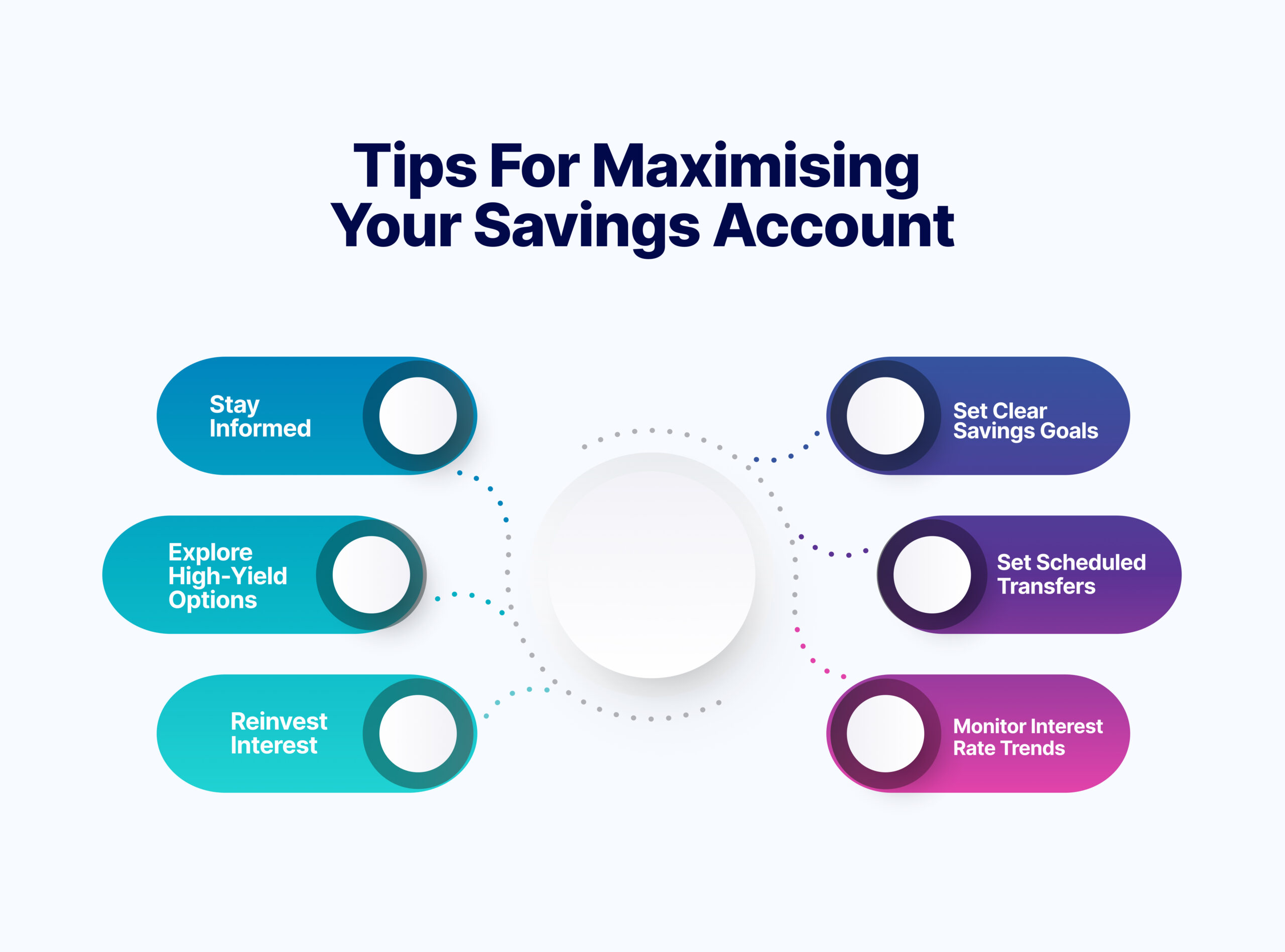
This section provides practical tips that can help you make the most of your savings and improve your financial well-being:
1. Stay Informed
Regularly check and stay informed about the rates offered by different banks in Nigeria. Banks may adjust rates based on economic conditions, and being aware allows savers to capitalise on favourable changes.
2. Explore High-Yield Options
Consider high-yield savings accounts or promotional offers from banks. These accounts often provide competitive rates that may surpass those of regular savings accounts.
3. Reinvest Interest
Consider reinvesting the interest earned back into the savings account. Reinvesting allows the interest to compound on a larger base, thus accelerating the overall growth.
4. Set Clear Savings Goals
Establish clear savings goals for emergencies, short-term needs, or long-term objectives like homeownership or education. Having specific goals provides direction and motivation for consistent savings.
Allocate funds into separate savings accounts for different purposes. This helps track progress towards each goal and avoids potential withdrawal of funds for specific needs that may derail you from your savings target.
5. Set Scheduled Transfers
Set up automatic transfers from a primary account to a designated savings account. Automated savings ensure consistency and discipline in building up your savings over time.
Explore mobile banking apps that offer features like round-up savings or automatic transfers based on spending patterns. These tools simplify the savings process and encourage regular contributions.
6. Monitor Interest Rate Trends:
Keep abreast of economic conditions and rate trends. Understanding the broader financial landscape helps in making informed decisions about savings and potential adjustments.
Be flexible and ready to adjust savings strategies based on changing economic conditions. What may be optimal during one period may need adjustment in response to changing situations.
Consistency, awareness, and strategic planning are key elements in building a solid foundation for your financial success.
The Right Savings Account For You
If you’re looking for a high-yield savings account that will help you withstand the effects of high inflation, we recommend a Mintyn Savings Account.
A Mintyn Savings Account offers you up to 18% interest on your savings. Options for other high-yield, fixed and flexible investment plans are also available at Mintyn Bank. You should try Mintyn today.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding rates and maximising savings in Nigeria involves a combination of knowledge, discipline, and adaptability.
By cultivating informed financial habits and actively managing savings, you can navigate economic uncertainties and work towards securing a prosperous financial future.
Remember, financial well-being is a continuous journey, and each step taken towards financial literacy and prudent savings practices contributes to long-term success.
Leave a comment to share your thoughts.








